Skin Type Photo Examples
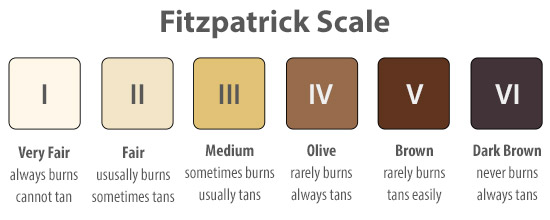

FITZPATRICK I
Typical Physical Features
- White, very pale, porcelain, ivory skin tone
- Red or blonde hair
- Light colored eyes (light blue, light green, grey)
- Freckles are common
- Example: fair-skinned Caucasian or Albino, Celtic
Reaction to Sun Exposure
- ALWAYS burns, blisters, and peels
- NEVER tans
FITZPATRICK II
Typical Physical Features
- White, fair skin
- Light colored hair
- Blue, hazel, or green eyes
- May have freckles
- Example: fair-skinned Caucasian, Scandinavian
Reaction to Sun Exposure
- Usually burns, blisters, and peels
- Tans minimally or with difficulty
FITZPATRICK III
Typical Physical Features
-
Cream white, peachy to beige or light olive skin tone
-
Any hair color
-
Any eye color
-
Example: darker Caucasian, European mix, lighter-skinned Hispanics or Asians
Reaction to Sun Exposure
-
·Sometimes burns
-
Tans gradually
FITZPATRICK IV
Typical Physical Features
-
Golden to olive or light brown skin tone (like caramel)
-
Usually dark hair and eyes
-
Example: Mediterranean, European, Asian, Hispanic, American Indian, sometimes mixed race African American
Reaction to Sun Exposure
-
Burns minimally
-
ALWAYS tans well
FITZPATRICK V
Typical Physical Features
-
Brown to dark brown skin tone
-
Dark hair and dark eyes
-
Example: Hispanics, African Americans, Middle Eastern
Reaction to Sun Exposure
- VERY RARELY burns
- Tans very quickly and easily
FITZPATRICK VI
Typical Physical Features
-
Deep mahogany to ebony or black skin tone
-
Dark hair and dark eyes
-
Example: African Americans, African, Middle Eastern
Reaction to Sun Exposure
-
NEVER burns
-
Deeply pigmented (tans quickly and deeply)
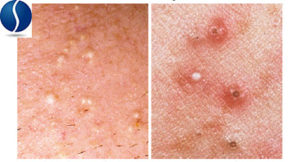
Basic Types of Acne Lesions
Acne is a term we use to describe inflammatory lesions that are red, raised, and sometimes painful. Inflammatory lesions that have puss visible through the skin are referred to as
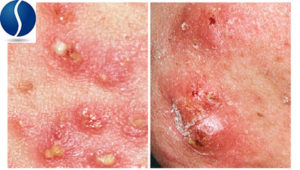
“Acne-prone ” people have non-inflammatory acne or “comedones” which refers to lesions, like blackheads and whiteheads that are slightly raised but are not red in color. A blackhead is an open pore clogged with oil and debris, while a whitehead is an obstructed pore that is enclosed by the skin.
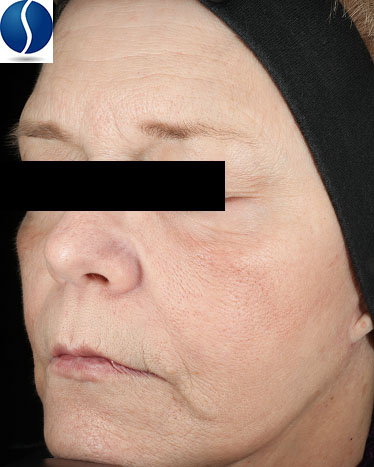
Facial Photoaging
Global facial wrinkles are defined as wrinkles in one or more areas including the forehead, glabella (between the eyes), crow’s feet (side of the eye), Under the eyes, nasolabial (between the nose and cheek area), around the lips, or marionette (extending downwards from the corners of the lips).
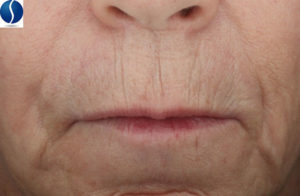
Lip Wrinkles
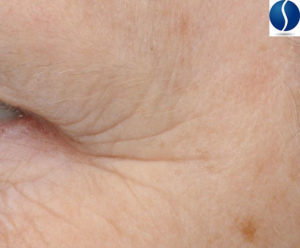
Crow’s Feet Wrinkles
Crow’s feet wrinkles are a wrinkle or wrinkles, that extend from the outer corner of the eye and extend beyond the orbital bone.
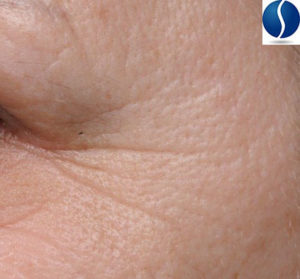
Undereye Wrinkles
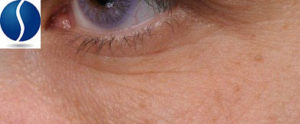
Mottled Pigmentation
Mottled hyperpigmentation consists of darkened areas, or patches, of skin on the face, commonly found along the hairline, jawline, or cheeks.
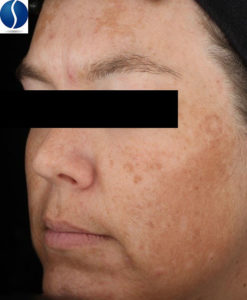
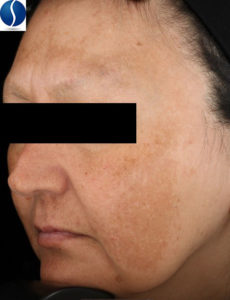
Age Spots
Age spots are flat areas of discrete hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) that can be any shape but must have well-defined borders. They are often seen in areas of the skin that the greatest sun exposure, like the face (cheeks, forehead and the back of the hands).
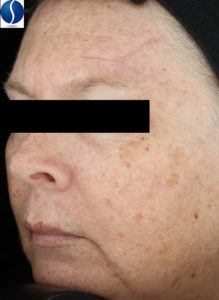
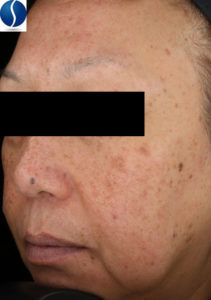
Melasma
Melasma is caused by hormonal changes and/or by sun damage and appears as symmetrical
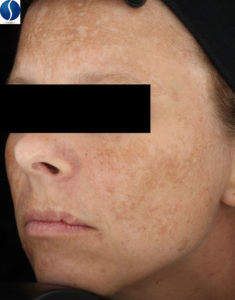
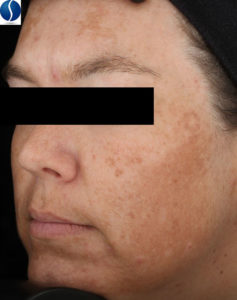
Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
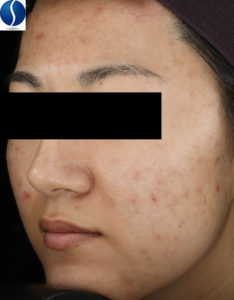
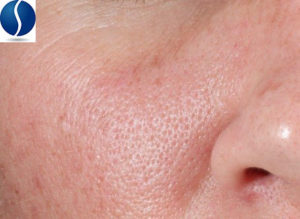
Enlarged Pores
Individuals with enlarged pores have indentations that appear on the surface of the skin on the cheeks, close to the nose.
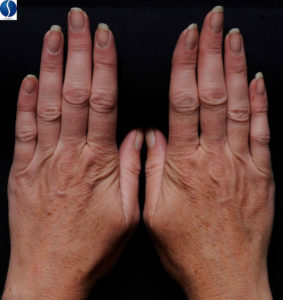
Hand Photodamage
Hand photodamage is due to sun exposure and environmental factors and can be seen by the emergence of age-spots (see below), thinning of the skin, and diffuse wrinkling that causes a surface appearance, similar to that of crepe paper.
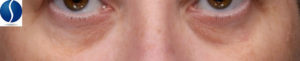
Under Eye Skin Conditions
Under Eye Bags and Puffiness
Under eye bags or “puffiness” is caused by fluid buildup under the eyes and loss of elastin, collagen, and muscle support.
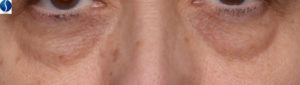
Under Eye Dark Circles
Under eye dark circles are caused by poor circulation of blood under the eye that creates a purple-to-blue appearance or a
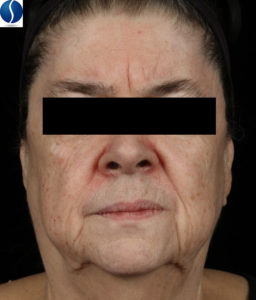
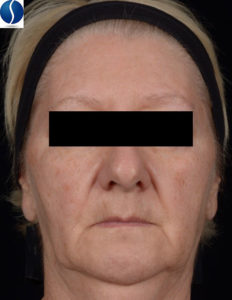
Facial Firmness and Sagging
Facial sagging is
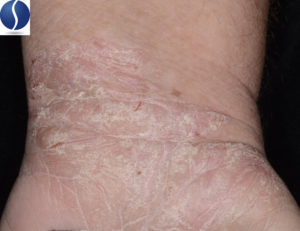
Eczema
Eczema is a chronically relapsing skin disease associated with erythema, scaly and oozing plaques, and severe itching. Signs and symptoms of eczema are associated with a compromised immune system and a defective skin barrier.